Beginner Options Knowledge
Bonus Topic: How to choose from the four basic strategies of options trading?
Once you understand the basics of options, you may be eager to try trading. So what strategies can I choose and how to choose? Let's start with a few of the most basic strategies.
Learning benefits: Unlock and join. There is one-on-one professional analyst to answer investment questions, and professional mooers share investment logic in real time. Let's learn more professional investment strategies>> Futubull official communication group There is a professional analyst to answer investment questions one-on-one, and professional mooers share investment logic in real-time to learn more professional investment strategies together.>>
Options can be divided into subscription and put options, and in the direction of trading, investors can buy or sell open positions.
So there are 2*2=4 basic opening strategies: Buy Long Call, Buy Long Put, Sell Short Call, Sell Short Put.
(Note: Opening positions and closing positions correspond to each other. (Opening refers to the creation of a new trading position, and closing refers to closing an existing position by trading the opposite.)
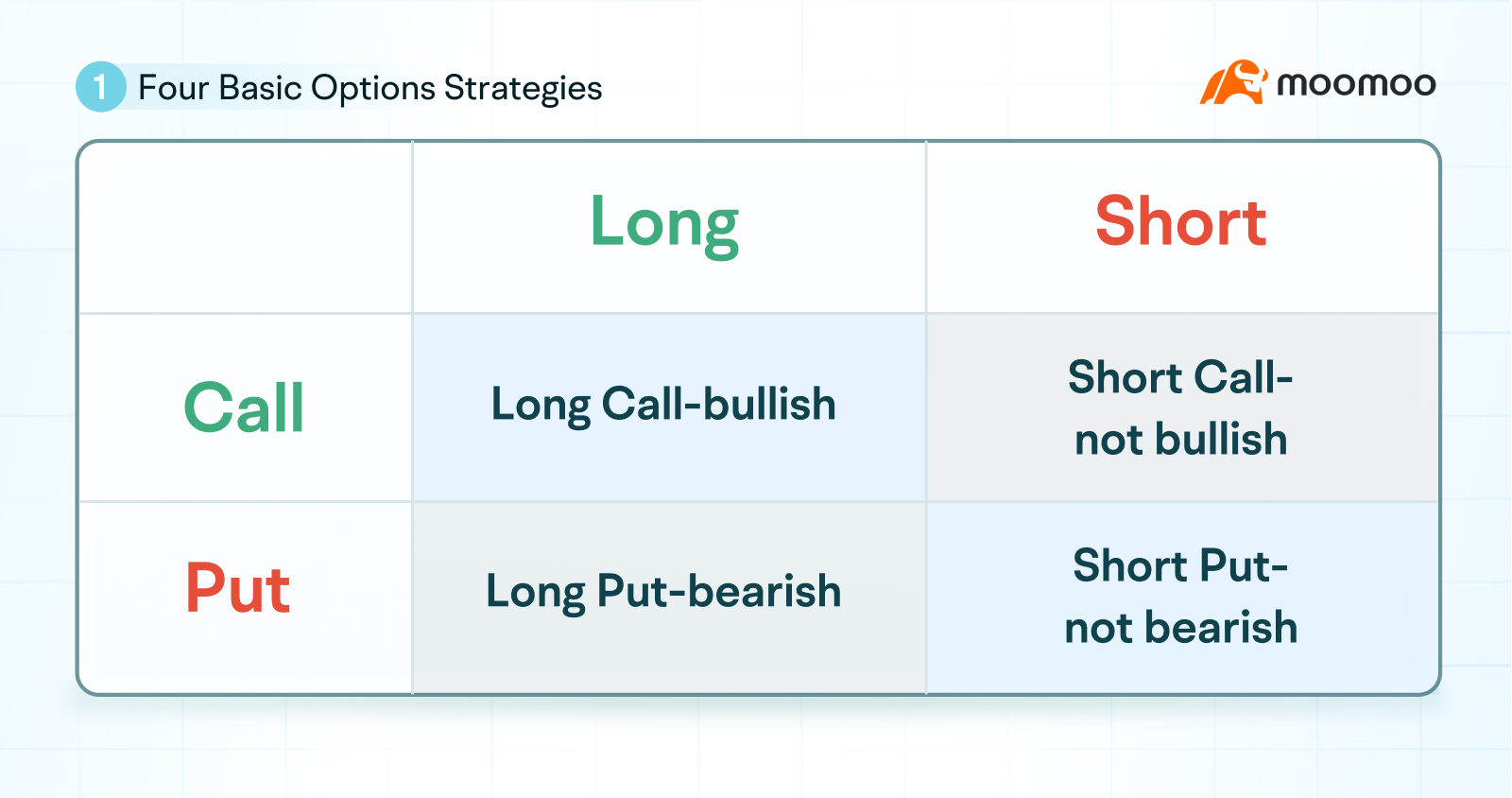
Simply put, these four strategies can be divided into two camps. One is the look/don't see camp, which includes Long Call and Sell Short Put. One is the underview/no-look camp, which includes buying Long Put and Short Call.
However, if we disassemble in detail, we will find that each strategy is different, let's see below.
Buy Subscription Options (Long Call)

Simple introduction
Buying subscription options requires payment of royalties at the beginning. After purchase, the investor has the right to purchase the agreed number of target shares at the exercise price within the specified period.
Applicable Scenarios
This strategy is usually used to take a good look at the target stock, to determine when the target stock is about to rise.
Earning conditions (assuming no transaction fees):
When the stock price rises as expected, investors have the right to buy the target stock at a lower price, making it profitable. The price of subscription options usually also increases as the price of the target stock rises, and it is also profitable to sell options to close positions. In theory, there is no upper limit to the potential profit, because it is possible by how much the stock price rises.
If the share price does not rise as expected, the investor loses the royalties paid to buy options. In theory, this is the potential maximum loss.
When the target stock price = option line price+option royalty, this strategy reaches a profit and loss balance.
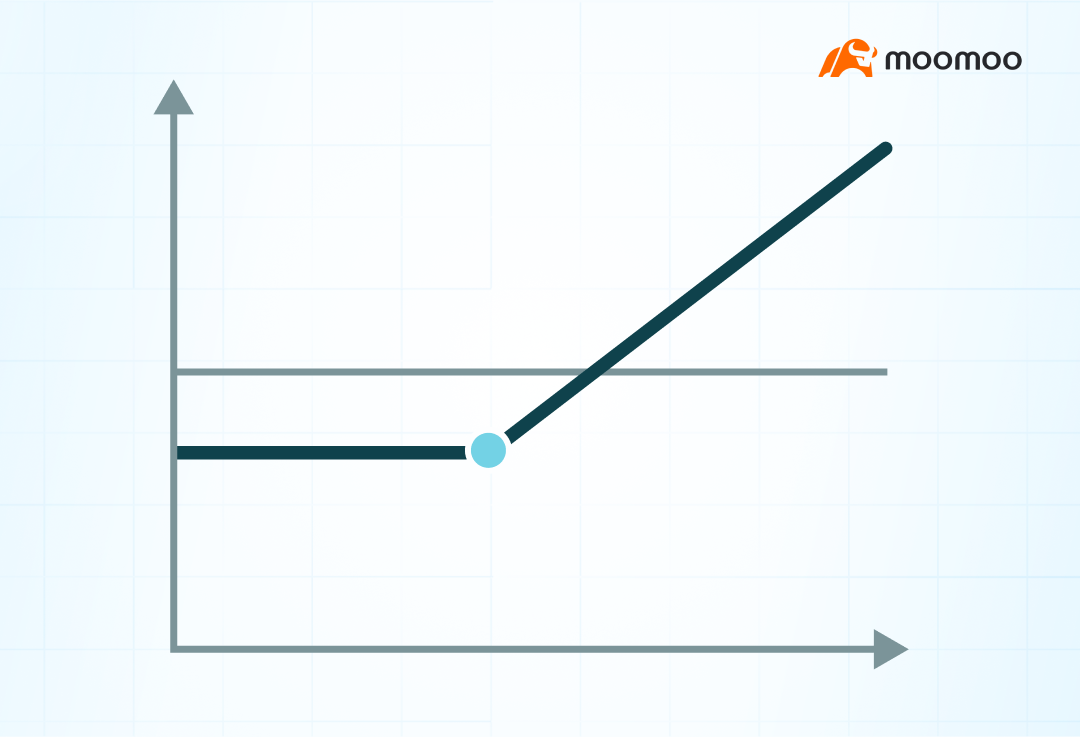
Relationship between time and extruded amplitude
Usually, the higher the price of the option - the further away from the expiration date, the higher the price of the option. The higher the pullback volatility, the higher the price of the option. So for buying subscription options, time attenuation and decrease in pullback volatility are unfavorable.
From this perspective, investors will often give themselves more remaining time to maturity when adopting this strategy and try to avoid high volatility options as much as possible.
How to play
After buying a subscription option, there are several possibilities for further actions: one is to look for the right opportunity, sell the option to close the position. The second is to exercise at the right time. Three is the expiration of the holding, and the option is void.
Investors usually don't want the latter to happen. While options still have time value, selling a closing position is usually cheaper than direct leverage.
In order to avoid too much loss of time value, some investors sell option closing positions with a certain amount of time left after the expiration date. There are also some investors who sell options to close positions when a stock falls and breaks a loss.
Pros and Cons
Compared to buying the target stock directly:
This strategy has less initial capital investment and is highly leveraged and allows for unlimited potential profit space when the stock price rises with relatively limited risk.
But the downside is that 100% of the invested funds will be lost if the judgment is wrong; if the judgment is correct, because the time value of the option is lost, the profit amount of this strategy will usually also be somewhat lower.
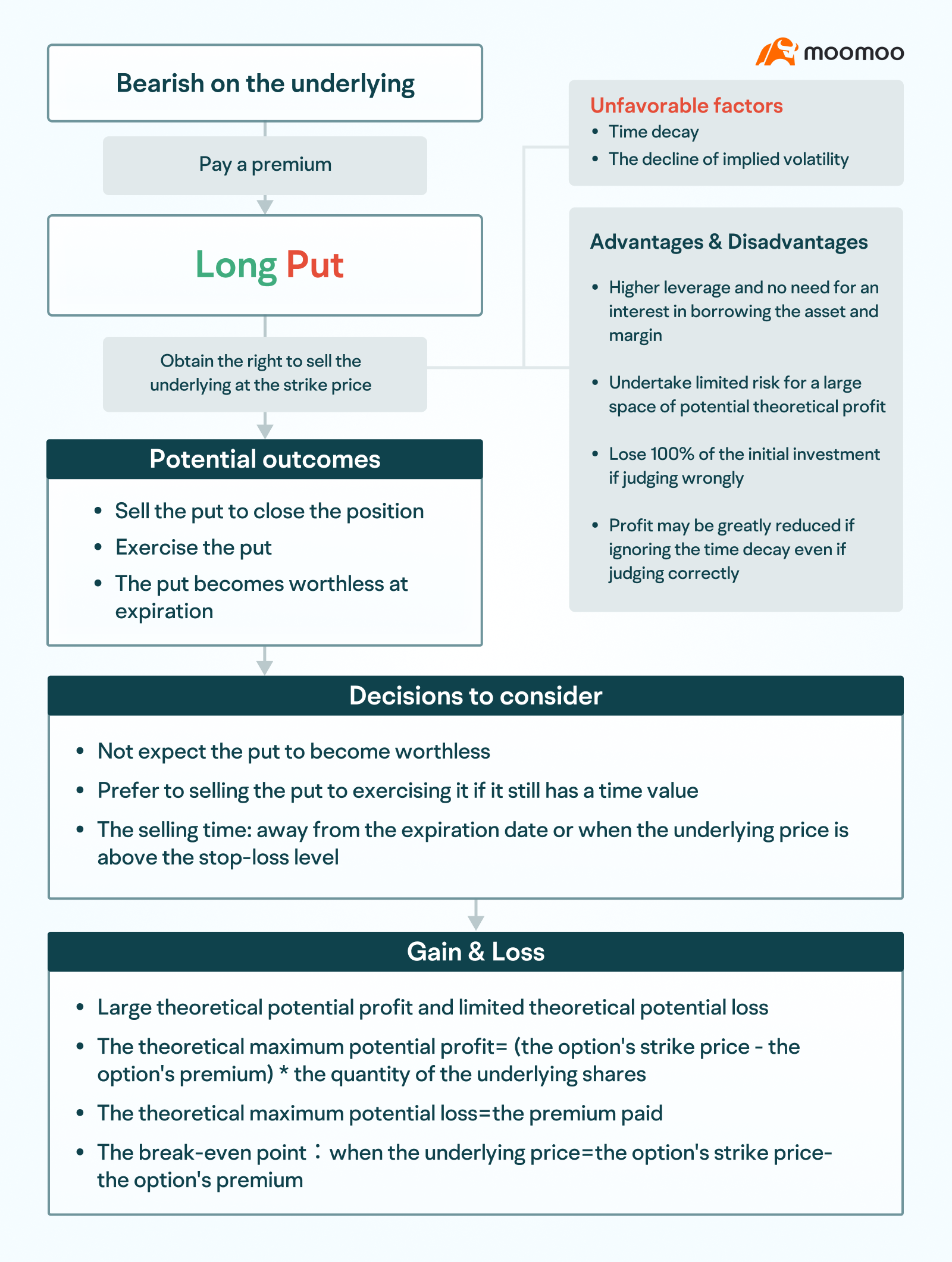
Buy Long Put
Simple introduction
Buying put options also requires a royalty payment at the beginning. After purchase, the investor has the right to sell a specified number of target shares at the exercise price within the specified period.
Applicable Scenarios
This strategy is usually used to understate the target stock, to determine when the target stock is about to fall. Some investors also buy put options while holding the target stock to hedge the risk of a fall in the target stock.
Earning conditions (assuming no transaction fees):
When the stock price falls as expected, investors have the right to sell the target stock at a higher price, making it profitable. The price of put options usually also increases as the price of the target stock falls, and it is also profitable to sell options to close positions. In theory, when the target stock falls to 0, the potential profit is greatest. Maximum Potential Profit = (Option Line Option Price - Option Royalties) * Number of Target Shares.
If the share price does not fall as expected, the investor loses the royalties paid to buy options. In theory, this is the potential maximum loss.
When the target stock price = option line option price - option royalty, this strategy reaches a profit and loss balance.
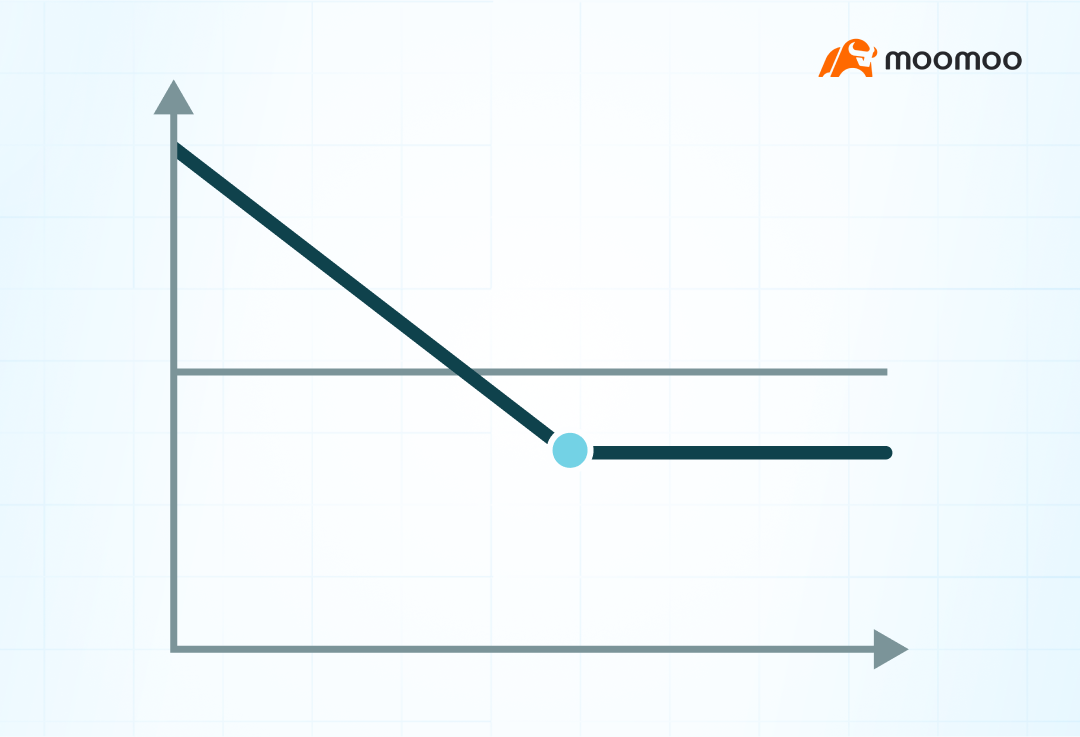
Relationship between time and extruded amplitude
In the same way as buying subscription options, time attenuation and decrease in pullback volatility are also unfavorable for buying short options.
From this perspective, investors will often give themselves more remaining time to maturity when adopting this strategy and try to avoid high volatility options as much as possible.
How to play
Similarly, after buying a put option, there are three possible subsequent actions: one is to find the right opportunity and sell the option to close the position. The second is to exercise at the right time. Three is the expiration of the holding, and the option is void.
When options still have time value, selling a closing position is usually cheaper than direct leverage. Some investors will take a stop loss when there is a certain amount of time left from the maturity date or when the target stock price rises to a certain position and sell options to close the position.
Pros and Cons
Compared to direct short selling of target stocks, this strategy does not require the payment of interest on margin and securities, is highly leveraged and allows for a relatively limited amount of risk, hedging a larger profit margin in the event of a stock price drop.
But if the judgment is wrong, 100% of the principal will be lost; if the judgment is correct, but if the loss of time value is ignored, profits may be greatly discounted.
Sell Subscription Options (Short Call)

Simple introduction
SELL SUBSCRIPTION OPTIONS AND INITIALLY RECEIVE A ROYALTY. After the sale, the investor is obliged to sell the agreed number of target shares at the exercise price at the exercise price. Also, because there is such an obligation, in order to prevent credit risk, the exchange requires the option seller to have a certain margin.
Applicable Scenarios
This strategy is usually used when the target stock is not looking good, judging that the target stock is about to fall or is relatively stable.
Earning conditions (assuming no transaction fees):
When the stock price falls or remains stable as expected and the option is not valued at maturity, investors can keep all the royalties initially received. This is also the biggest potential gain in theory for this strategy.
If the stock price rises, the profit and loss balance when the target share price = option line price+option royalty.
If the share price continues to rise, investors will suffer losses. In theory, the potential loss is limitless because of how much the stock price rises is possible.
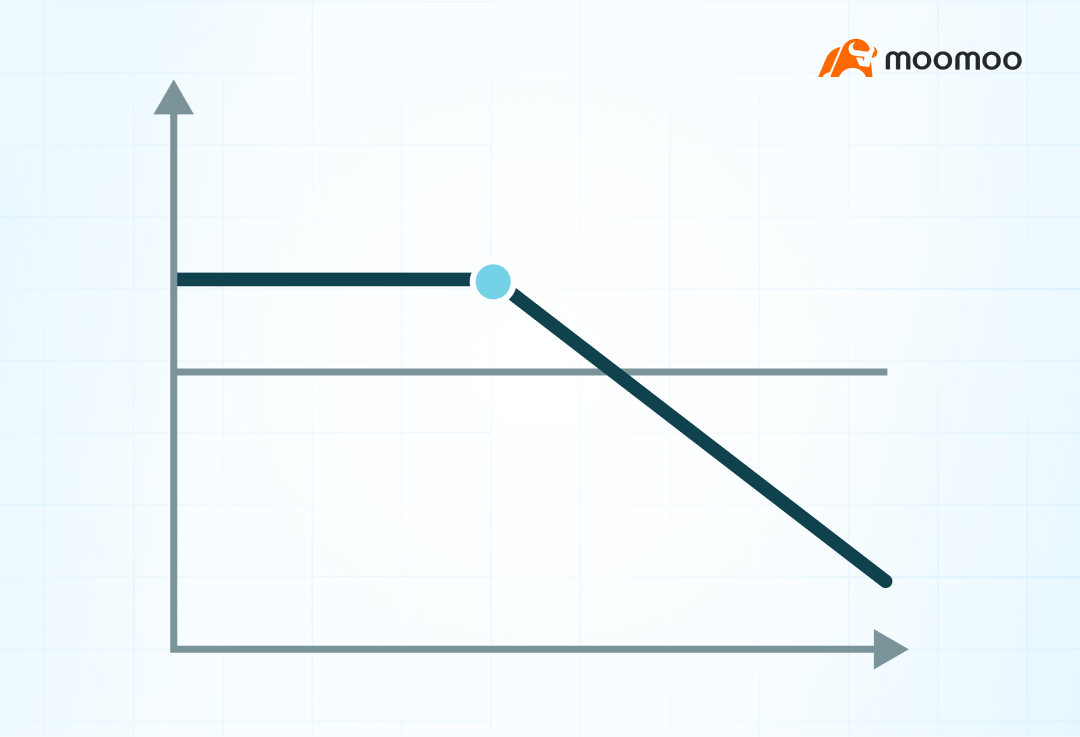
Relationship between time and extruded amplitude
For the sale of subscription options, time attenuation and a decrease in the pullback in volatility are favorable.
From this perspective, investors may be inclined to choose options that are shorter in distance or with higher volatility.
How to play
After selling the subscription option, there are several possible subsequent actions: one is the expiration of the holding and the option is void. The second is to stop losing at certain times and buy options to close the position. Three is to be enforced.
The first case is what investors are most hoping for. But if the judgment is wrong, the opposite of what is expected, in order to avoid being exercised, when the stock price rises to a certain position, some investors will choose to buy the option to close the position, thereby stopping the loss.
Pros and Cons
If judged and operated correctly, this strategy will generate income for investors, profiting from a drop in the share price or a regional shock.
But since the potential losses are unlimited, and there is a risk of forced closing if the margin is insufficient, this strategy is actually quite risky. In practice, it is not recommended for beginners to use this strategy alone.
To control risk, investors may use this strategy in conjunction with other positions. For example: If you hold a target stock and feel that the share price has risen to $X, you can sell a subscription option with an exercise price of X. In this way, you can both get royalties and possibly ship smoothly.
Sell Short Put

Simple introduction
When the put option is sold, the investor is obliged to buy the agreed number of shares at the exercise price at the exercise price upon the initial sale of a royalty. Likewise, a certain margin is required.
Applicable Scenarios
This strategy is usually used when the target stock is not understated, to determine whether the target stock is about to rise or is relatively stable.
Earning conditions (assuming no transaction fees):
When the stock price rises or remains stable as expected and the option is not valued at maturity, investors can keep all the royalties initially received. This is also the biggest potential gain in theory for this strategy.
If the share price falls, the profit and loss balance when the target share price = the option line price - the option royalty.
If the share price continues to fall, investors will suffer losses. In theory, when the share price falls to 0, the potential loss is greatest. Maximum Potential Loss = (Option Line Option Price - Option Royalties) * Number of Target Shares.
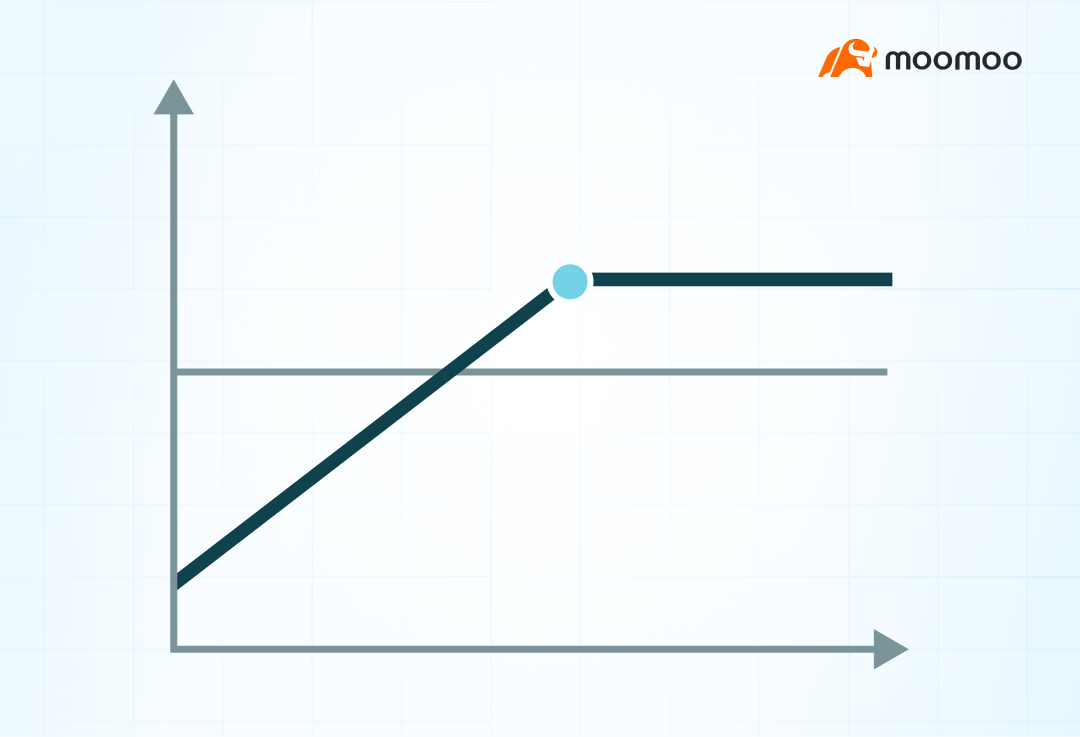
Relationship between time and extruded amplitude
For the sale of put options, time attenuation and a decrease in the pullback in volatility are favorable.
From this perspective, investors may be inclined to choose options that are shorter in distance or with higher volatility.
How to play
After the sale of the put option, there are several possible subsequent actions: one is the expiration of the holding and the option is void. The second is to stop losing at certain times and buy options to close the position. Three is to be enforced.
The first case is what investors are most hoping for. But if the judgment is wrong, the opposite of what was expected, and in order to avoid being exercised, when the stock price falls to a certain position, some investors will choose to buy the same option to close the position, thereby stopping losses.
Pros and Cons
If judged and operated correctly, this strategy generates income for investors, profiting from share price rises or regional shocks.
But because of the large potential losses and the risk of being forced to close the position if the margin is insufficient, this strategy is actually quite risky. In practice, it is not recommended for beginners to use this strategy alone.
The situation is somewhat better if investors intend to buy a target stock near the option's line price.
summed
Finally, we summarize the main characteristics of these four basic strategies for easy comparison.
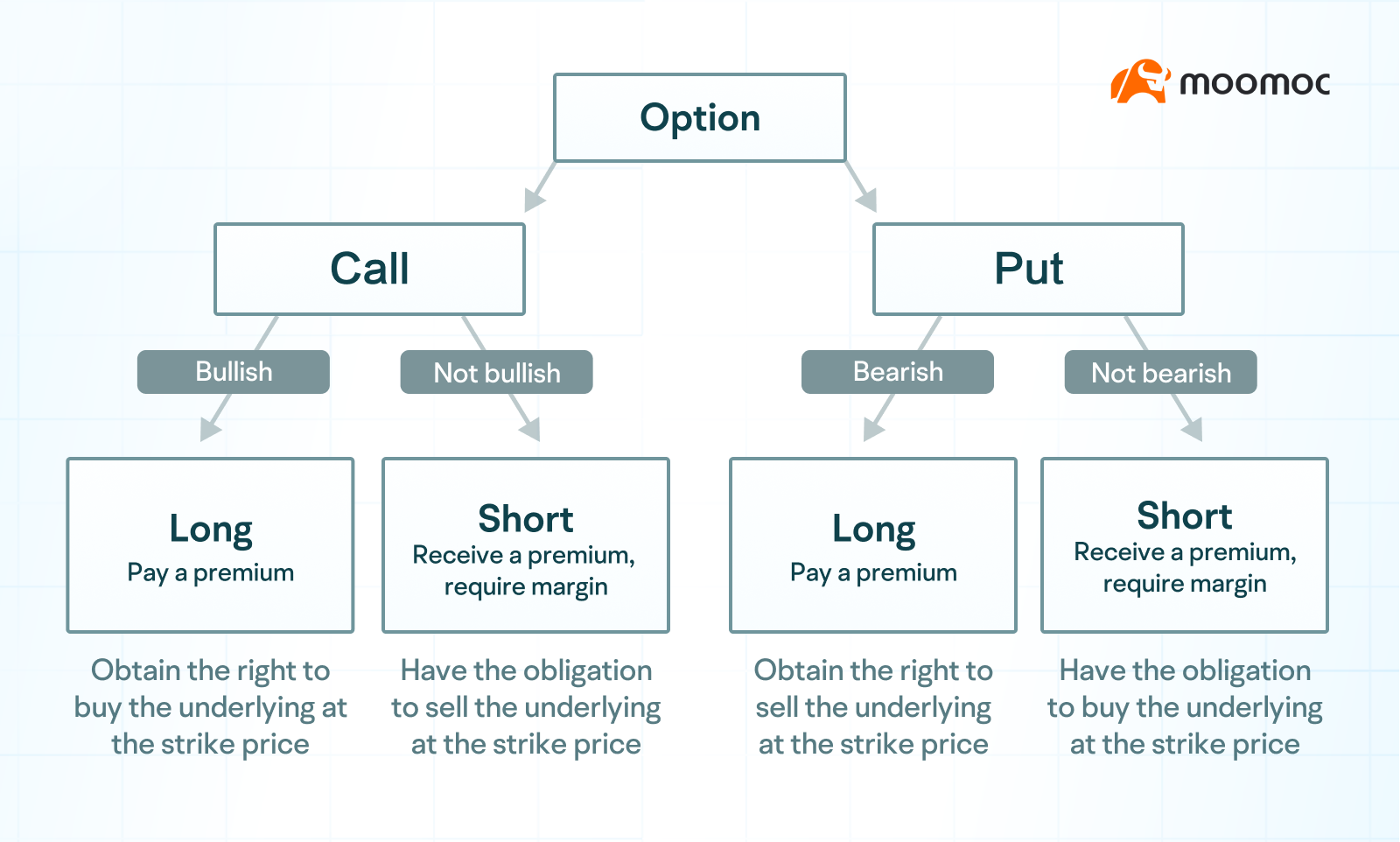

The above is the content of this lesson. Have you mastered all four basic strategies regarding options? Feel free to share your thoughts in the comments section.

